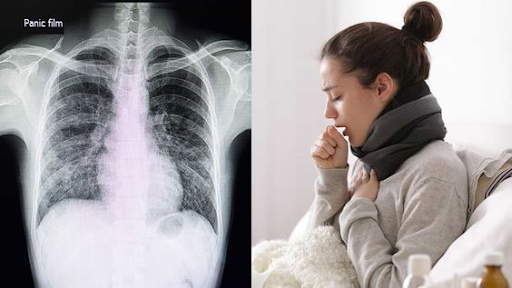
Pneumonia is an illness that causes the air sacs in the lungs to fill with fluid or pus, making breathing difficult. The most frequent symptoms are a dry or phlegmy cough, fever, chills, and tiredness. Other symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, chest discomfort, and shortness of breath. Shortness of breath, disorientation, reduced urine, and lightheadedness are symptoms of a more serious illness. Pneumonia causes 1.3 trips to the ER and 50,000 deaths in the United States each year.
With the COVID-19 epidemic still affecting individuals all over the world, pneumonia has become an even bigger public health problem. Some persons with COVID-19 have no symptoms, while others may have fever, body aches, dry cough, tiredness, chills, headache, sore throat, lack of appetite, and loss of smell. Overwhelming COVID-19 viral infection, severe inflammation, and/or subsequent bacterial pneumonia can all harm the lungs.
Here are some other facts regarding pneumonia that you should be aware of:
Anyone Can Get Pneumonia
While some people are at a higher risk than others, pneumonia may affect anybody. Fever, wheezing, cough, chills, fast breathing, chest pains, lack of appetite, and malaise, or an overall sense of weakness or bad health, are all symptoms of pneumonia.
Both children and the elderly are at risk. Young children and elderly people (over the age of 65) are the most vulnerable to pneumonia and its consequences. Pneumonia affects around one million people each year, and it is the greatest cause of hospitalization and mortality in children under the age of five worldwide.
Determining The Cause Of a Case Has Become Simpler And Faster
According to Michael Bachman, M.D., Ph.D., the time it takes a well-equipped testing facility to identify which virus or bacteria is causing someone sick has decreased from more than a day to only hours in the last few years.
The rapid pace of identification, enabled by modern genetic tests performed by specially trained personnel such as those Bachman supervises at the University of Michigan Health System’s clinical microbiology lab, means doctors can obtain more precise information to help them choose the best treatment for each patient.
Currently, this testing is mostly used for hospitalized patients, but it may one day be used to guide the management of less severe situations.
You Can Safeguard Yourself And Your Loved Ones
Many of the diseases that might lead to pneumonia can be prevented using vaccines. Other methods include:
- Wash your hands and cover your cough and ensure you sanitize your hands frequently.
- Every year after the age of six months, obtain a flu vaccine. It lowers your chances of getting the flu, which can lead to pneumonia.
- If you have a newborn or toddler, make sure he or she gets all of his or her vaccinations on time. This can guard against infections that can lead to pneumonia and other complications.
- If you or your kid have any additional health concerns, see your doctor about the appropriate vaccinations for you. People of any age who have diseases such as asthma, diabetes, heart disease, or lung disease are included.
Take Action If You Believe You Have It
Symptoms such as fever, chills, and cough might indicate a variety of conditions. It will take some investigation to determine whether you have pneumonia, what is causing it, and the best therapy for you.
- To assist doctors and nurses in their care:
- Take your temperature and make a mental note of the color of your phlegm.
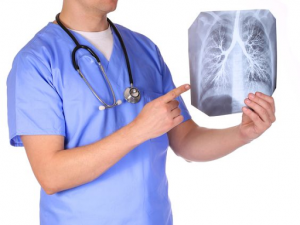
- Visit your doctor for a checkup and perhaps a chest X-ray to check for indications of infection and take blood pressure monitoring.
- If you are given antibiotics, take them exactly as prescribed. If you stop too soon, the strongest bugs may survive, allowing them to return or infect others.
- If you’re taken to the hospital or even your doctor’s office, you’ll be required to cough out a good quantity of phlegm.
Causes Lung Damage
COVID-19-acquired pneumonia can result in long-term lung damage. While most individuals who recover from pneumonia do not have long-term lung damage, pneumonia caused by the coronavirus is frequently more severe and can result in long-term symptoms or a kind of lung failure known as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). While in the hospital, patients with ARDS may be placed on a ventilator to assist oxygen flow throughout the body. ARDS can result in pulmonary scarring and be deadly.
Research and New Technologies Will Improve Pneumonia Prevention And Treatment In The Future
The vaccines we have today are the result of the study, and research has shown that after one of the newer immunizations was introduced, the number of illnesses from resistant strains of the most frequent bacterial cause of pneumonia reduced.
Rapid diagnostic tests are becoming increasingly essential in the fight against antibiotic resistance. If we can rapidly determine whether a pneumonia case is caused by bacteria or a virus, we can treat it with extremely focused medicines rather than broad-based ones that may develop resistance.
For patients in critical conditions who require oxygen support, research has shown that molecular sieve manufacturers for oxygen generators have played a key role in the supply of highly purified air supply to critical patients.
Conclusion
Pneumonia prevention and treatment need good primary health care as well as active and empowered communities. We hope that the information provided above is beneficial to you.