The regularity of the uterus is important in pregnancy. But many abnormalities can occur in a woman’s uterus which can be in its size, shape, and structure. The following article explains one of the abnormalities of the uterus which is the septate uterus and also explains the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment of the septate uterus.
What Is A Septate Uterus?
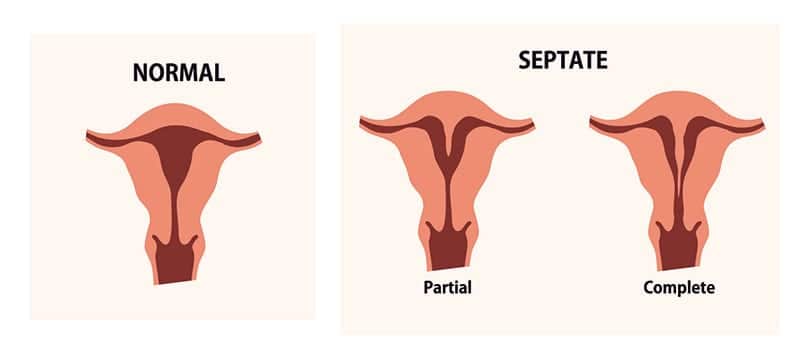
A deformity in which a membrane which is known as septum divides the uterus into two portions at its middle is the septate uterus. This septum can be thick or thin as it is a muscular and fibrous band.
There is an increased risk of miscarriages in a woman with a septate uterus. The exact reason behind this is not known, but it is estimated that the septum cannot provide the proper support needed for a safe pregnancy. Pregnancy is also interfered with by the septum in a variety of other ways. Surgery is the option to treat this condition.
Sometimes the septate uterus is misdiagnosed with bicornuate uterus. In the bicornuate uterus, the uterus from the top or fundus dips in towards the midline of the uterus. The pregnancy of a woman is not affected by the bicornuate uterus unless the dip is extreme.
Effect Of The Septate Uterus On Pregnancy
A woman’s ability to conceive is not affected by the septate uterus, but the risk of miscarriage is significantly increased due to the septate uterus. There can be recurrent miscarriages in a woman who has a septate uterus.
There are 10 to 20 percent chances of miscarriage in women who are pregnant. The most common type of abnormal uterine development is septate uterus. It is estimated that a septum in the uterus covers half of the developmental problems of the uterus.
The risk of both miscarriage and recurrent miscarriage is increased in a woman who has a septate uterus. Pregnancies which occurs with any type of uterine abnormality increase the risk for:
- Preterm labor
- Birth via cesarean delivery
- A breech position, which means the bottom of the baby is facing down before birth
- Bleeding complications after delivery
The risk of miscarriage is increased because of irregular uterine contractions or reduced uterine capacity.
There are greater chances of developing birth defects in babies who are born to mothers with a septate uterus. In fact, according to one study, this risk of birth defects is four times higher in those who are born to a woman with a septate uterus as compared to a woman without this condition.
If a woman is pregnant and has septate uterus, then her pregnancy is treated as high-risk. Her pregnancy is monitored carefully by her doctor. Frequent ultrasounds are performed by the doctor to check the position of the baby, because the baby may settle in a breech position.
Symptoms Of A Septate Uterus
There can be an irregular uterus in around 3 percent of women. This irregularity can be in the size of the uterus, its structure, or its shape. Among all the irregularities, one of the most common ones is the septate uterus.
Women with a bicornuate uterus are born with it, but they may not be aware of it, because there are no symptoms that make them feel unusual. They discover this condition after an ultrasound.
On the other hand, a woman with septate uterus may experience the following symptoms:
- Pain during sex
- Painful periods
- Irregular vaginal bleeding
- Repeated miscarriages
- Discomfort or pain in the abdomen
Causes Of Septate Uterus
This is a congenital abnormality, which means it’s something a woman born with. A woman’s uterus develops when she is in her mother’s womb, so if her uterus does not develop normally it means a uterine defect can occur. The prevention of this condition is impossible.
When there is an abnormal development of paramesonephric ducts then the septate uterus develops. The uterus is divided into two projections, giving a heart-shaped appearance when the ducts fail to fuse correctly.
Diagnosis
A woman should consult a doctor if she experiences repeated miscarriages, irregular vaginal bleeding, or painful periods. The doctor performs the following tests to diagnose septate uterus:
- Pelvic examination
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
- Ultrasound where the image of the uterus is created using high-frequency sound waves
- X-ray or hysterosalpingogram
Treatment
Surgery is done to treat septate uterus, which is known as metroplasty. Nowadays hysteroscopic procedures are done to treat septate uterus in which there is no need for an outer abdominal incision.
A lighted instrument is inserted into the uterus through the vagina during a hysteroscopic metroplasty. To cut and remove the spetum another instrument is also inserted.
Time taken by this technique is about one hour and is minimally invasive. Women who are treated with a hysteroscopic metroplasty return home on the same day of the surgery.
About fifty to eighty percent of women with a history of repeated miscarriages will have a safe future pregnancy after this surgery. And women who were previously unable to get pregnant may be able to become pregnant after this surgery.