Cancer is a disease in which body cells proliferates uncontrollably and destroys body tissues. This uncontrollable change in body is due to mutation in DNA that is present within the cells. The DNA is packaged into large number of genes and each gene contains a set of information telling a cell how to function, as well as how to grow and divide.
The mass of proliferated cells is known as tumor. A tumor can be benign or malignant. A malignant tumor is which grow and spread to other parts of body. A benign tumor is which only grows but not spread.
In this article, there is detailed information about the cervical cancer, which is very important for every female.
What Is Cervical Cancer?
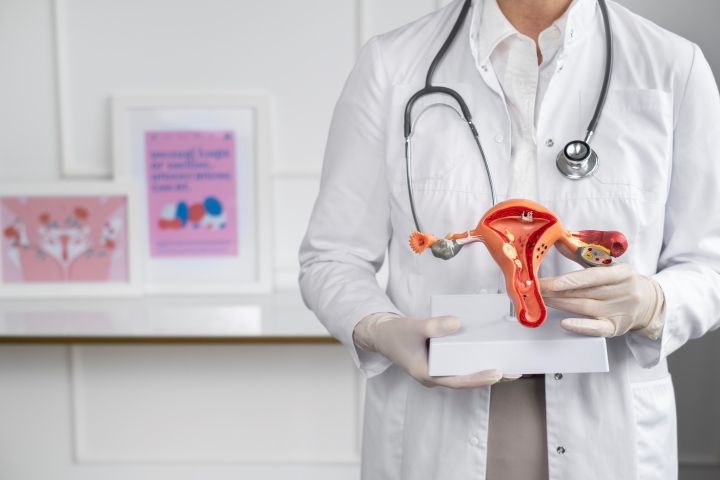
The lower part of uterus is cervix that connects vagina to the uterus. When cells of cervix starts proliferating without any control, cervical cancer takes place. When the cells of cervix go through changes such as dysplasia, in which abnormal cells begin to appear in cervix and if these cells are not destroyed over time, they become cancerous and spread more deeply into the cervix.
The cervix has two parts:
- The outer part of the cervix is known as ectocervix. This part is lined by thin cells called squamous cells.
- The inner part that connects vagina and uterus is called endocervix. Mucus is present in this part and is lined by columnar cells.
The border where the above parts of cervix meet is transformation zone, which is also called as squamocolumnar junction. This is the area where most of the cervical cancer begins.
Types Of Cervical Cancer
Name of cancer depends on the cell from which it starts. There are two main types of cervical cancer, which are as follows:
- Squamous cell carcinoma: Most of the cervical cancers are of this type. Cells of ectocervix divide and give rise to these cancers.
- Adenocarcinoma: Glandular cells of the endocervix give rise to cervical adenocarcinomas.
- Mixed: When cervical cancer has features of both squamous and adenocarcinoma, this is known as mixed carcinoma or adenosquamous carcinoma.
Risk Factors
Risk factors of cervical cancer are as follows:
- Smoking: Risk of cervical cancer is high in those who smokes. When a person who smokes is infected with HPV , the infection lasts logner.
- Variable sexual partners: Early age of marriage and multiple sexual partners both are the risk factors for HPV infection and so on for cervical cancer.
- Sexually transmitted infections: Other STIs which can be due to Chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis etc. can increase the risk of HPV, which can further lead to cervical cancer.
- Weak immune system: Immunity plays important role to defend our body from infections. If immunity of an individual is low then there will be more risk of HPV infection, following cervical cancer.
Signs And Symptoms Of Cervical Cancer
- Vaginal discharge which can be bloody or watery.
- Bleeding from vagina after intercourse, between mensus or after menopause.
- Heavy menstrual cycle.
If cancer spread to other organs and nearby tissues then following symptoms can be observed:
- Painful micturition, sometimes blood may also present in urine.
- Blood in stool and painful defecation.
- Weakness, weight loss and loss of appetite.
- Pelvic or lower abdominal pain.
Screening Of Cervical Cancer
Screening of cervical cancer is done by Pap test and HPV DNA test, among these Pap test is very important.
- Pap test: Pap test is done by making Pap smear. To make a Pap smear cells from the surface of cervix collected and then after adding a fixative, the lab technician looks them under a microscope. Pap smear examination should start at age of 21.
Pap test should be done in every three years in women between age 21 to 65.
- HPV DNA test: Cells from cervix are taken and a lab technician looks these cells if they are infected with HPV that may lead to cervical cancer. DNA testing is done simultaneously when Pap smear test results abnormal.
Diagnosis Of Cervical Cancer
If Pap smear and HPV DNA tests show abnormality then some other tests need to be done to confirm cervical cancer. These tests are as follows:
- Colposcopy: Cervix is stained with acetic acid, then cells of cervix seen in colposcope. It is done when tests of Pap smear results unsual. Colposcope magnifies cervix by 8-15 times. This is done in OPD. If colposcopy shows signs of cancer then further biopsy is to be done.
- Biopsy: Tissue sample is removed from the cervix and then check it under microscope for cancer. There are many types of biopsies such as punch biopsy, LEEP ( loop electrosurgical excision procedure), endocervical curettage and cone biopsy.
In case of invasive cancer some other investigations are done which are as follows:
- Chest X-ray to see spread in lungs.
- Blood tests such as CBC, LFT etc. to see involvement of liver.
- Intravenous pyelogram or CT scan to check urinary tract, and cystoscopy to see urinary bladder and urethra.
- CT, MRI, or PET scan for lymph nodes.
Staging Of Carcinoma Cervix
- Stage I – limited to cervix
- Stage II – involves upper two-third of vagina
- Stage III – spreads to lower one-third of vagina
- Stage IV – metastasis in bladder bowel and distant metastasis.
Treatment Of Cervical Cancer
Depending on stage, age, health there are many treatment options available for cervical cancer such as radiation, chemotherapy, surgery etc.
Radiation: EBRT (external beam radiotherapy) and Brachytherapy are two types of radiation therapy which uses energy beams to kill cancerous cells.
Chemotherapy: Certain drugs are given which kills cancer cells. The schedule and the type of drug which is to given depends on where the cancer is located.
Surgery: Some common surgeries of cervical cancer are:
- Laser surgery which uses laser beam to kill cancer cells
- Cryosurgery which freezes cancer cells
- Cone biopsy
- Simple hysterectomy which involves removal of uterus only
- Radical hysterectomy with pelvic lymph node dissection
- Trachelectomy which removes cervix and upper vagina but not uterus
Immunotherapy: Medicines are used to boost immune system so that cancer cells can be recognized and destroyed.
Prevention Of Cervical Cancer
Regular gynecological examination and Pap tests are important to prevent cervical cancer. Other ways by which this can be prevented re:
- HPV vaccination: There are certain vaccines available against HPV such as cervarix, gardasil etc. so every eligible female should get vaccinated.
- Protected sex and limit sexual partners
- Avoid smoking
Prognosis
When there is early detection and treatment the survival rate of cancer cervix is 100%. If it remains undetectable then rate depends on stage of cancer. If the cancer has spread to other tissues then the survival rate becomes 58%.
Resources:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2018789/