What exactly is Sickle cell anemia?
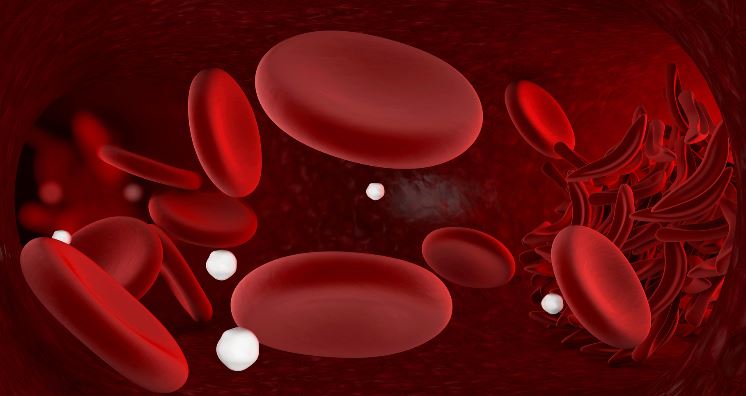
Anemia is a condition where the total red blood cell count in the body decreases. Sickle cell anemia is its subtype. This phenomenon is most common in the African, Mid-Eastern and Latin American gene line. Sickle cell anemia foster when there arises a mutation in the gene. Scientists claim that mutation may have arose in the areas where malaria was prevalent. The basis of this thinking is that kids with sickle cell anemia are relatively tolerant to malarial infection. It is a genetic abnormality wherein there is a defective production of hemoglobin. A normal hemoglobin molecule has 2 alpha and 2 beta chains. While the patient of the disease has abnormal gene for the production of the beta chain. The abnormal hemoglobin thus is incompetent to carry oxygen to the body tissues.
Everything You Need to Know About Sickle Cell Anemia
Normal RBCs are round and flexible while sickle cells are stiff and crescent moon or sickle-shaped, they are sticky as well. Stickiness increases their liability to form clusters while due to their crescent shape they are likely to be stuck in blood vessels and hamper blood flow plus the oxygen binding capacity of the hemoglobin molecule present in the RBC is greatly decreased. If a cell blocks the blood vessels it causes pain and there are occurrences of cramps in the extremities. The low blood oxygen supply to the organs increases the chances of organ failure. Also, the normal RBCs have a lifespan of 120 days while the sickle cells live for 10-20 days only.
Signs and Symptoms:
Proper diagnoses is a necessity in this type of anemia while some indications are:
- Anemia
- Episodes of pain due to occlusion of blood vessels
- Frequent Jaundice
- Acute chest pain
- Strokes if blockage of vessels supplying brain
- Splenic sequestration and its damage
- Dehydration
Sickle cell anemic children have this inborn disease only if both of his/her parents present with one copy of the minor trait of the sickle cell gene in their genetic makeup. When the child inherits this minor trait from both of its parents he develops the disease. This phenomenon is known as recessive trait inheritance and its expression is as a result of 2 minor traits coming together. Therefore this defect will always be present in the hierarchy. Complications in such children include increased susceptibility to infection. Bone, eye, kidney and all other organ damage can occur due to inadequate blood supply.
The severity of the sickle cell anemia depends upon the degree of defectiveness and the amount of defective gene present in the gene pool.
Several types include:
- Sickle cell anemia
- Sickle cell anemia with hemoglobin C
- Beta thalassemia
- Other types
It is but obvious there are innumerable of complications associated with this disease. Though do not worry about your child’s academic performance as it would be no different than of its peers. Although silent strokes may occur which cause memory and thinking problems; if their frequency is more then there may precipitate neurological disorders with degrading mental function. Extra-curricular and sports activities participation should be encouraged up to their tolerance level. The result can be to their best of the abilities with right frequency of rest and plenty of water consumption. No doubt compared to other children your child will tire faster.
Strategic management:
Most treatment and management strategies are aimed to relieve the symptoms and preventing further complications. So the preventive measures are as follows:
- Anemia can be managed by diet to increase red cell count and hemoglobin content of the body. Folic acid supplements will help too. In severe anemic cases, blood transfusion is recommended by physicians.
- Dehydration and pain go hand in hand. Increasing the water uptake provides proper circulating blood and minimize the chances of any occlusion by sickle cells.
- Usually the iron uptake of the body should be increased in anemia but in this case, it can complicate the situation. There would be an iron overload in the blood if the kid has been transfused blood. Removal of this extra iron is therefore required as it can create toxicity.
- Usually, there is splenic sequestration due to blood pooling in the spleen. Blood transfusion dilutes the sickle cell hemoglobin concentration and thus removes trapped blood.
- Regular vigilance of infection and fever should be indispensable as this may turn into serious issues.
Crisis situation:
If your child is already diagnosed with sickle cell anemia do not forget to call the doctor in any of the following emergencies:
- Breathing problem
- Severe headache
- Inability to speak
- Weakness and pain in extremities
- Pain in the chest
- Seizures
- Persistent vomiting
- Unexplained lethargy and unconsciousness
- Fever above 39 degree Celsius
Hope this article was of help for all our parents!! Please share your comments/queries/tips with us and help us create a world full of Happy and Healthy Babies!!