A hernia is defined as a protrusion of an organ through an opening into the muscle or tissue that holds it in place. For instance, the intestine may break via a weakened area in the abdominal wall. Most of the hernias occur in the abdomen between the chest and the hips but may also be seen in the upper thigh and groin areas. Many herniae cause no threat to life, but they require treatment and do not go away on their own. Surgeries are required to deal with dangerous complications.
In this article:
What is an Umbilical Hernia?
Causes of Umbilical Hernia
Symptoms of Umbilical Hernia
Diagnosis of Umbilical Hernia
Complications of Umbilical Hernia
Treatment of Umbilical Hernia
Surgery for Umbilical Hernia
All You Need to Know about Umbilical Hernia
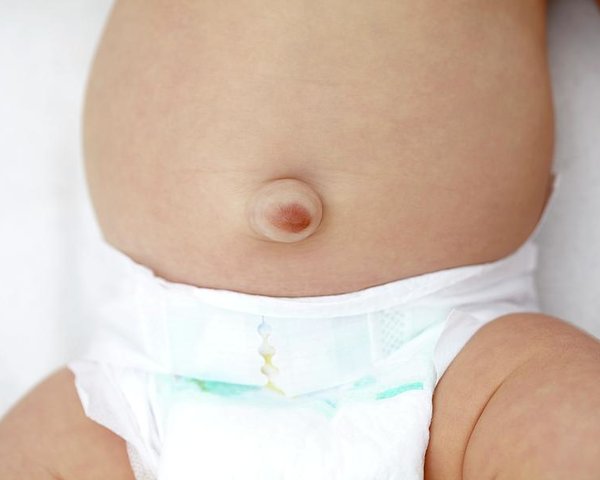
What is an Umbilical Hernia?
The baby inside the mother is connected to her via the umbilical cord during pregnancy. This cord passes through a small opening between the abdominal wall muscles. Usually, the opening closes soon after delivery. But sometimes, an umbilical hernia can occur when the abdominal wall layers cannot join completely and the intestinal tissue or any other tissue from the abdominal cavity protrudes through the weak spot around the umbilicus (belly button). Almost 20 percent of babies are born with an umbilical hernia.
Such types of hernias are often painless and cause no discomfort to the baby. In about 90 percent of cases, the umbilical hernias will close on their own. If the umbilical hernia does not close by the 4 years of age, then it requires treatment.
Causes of Umbilical Hernia
An umbilical hernia is seen when the opening in the abdominal muscles allows the passage to the umbilical cord but fails to close completely. Umbilical hernias are very common in babies but may be seen in adults also. Pre-mature babies, low birth weight babies are at high risk of developing an umbilical hernia. It affects both males and females equally.
In adults, an umbilical hernia occurs due to the high amount of pressure exerted over the weak section of abdominal muscles. Following are the potential causes :
- Being overweight
- Excessive fluid retention in the abdominal cavity
- Frequent pregnancies
- Having multiple gestational pregnancies
- Undergone abdominal surgeries
- Persistent heavy coughing
Symptoms of Umbilical Hernia
Umbilical hernias are seen when the baby cries, laughs, or is straining to use the bathroom. The most believed symptom is swelling or bulge around the umbilical area, which might often disappear when the baby is relaxed. In children, it is often observed that umbilical hernia is painless.
Adults may also suffer from this. The main symptom in them remains the same i.e. swelling or bulge near the belly button. But in adults, umbilical hernia is associated with pain and discomfort and therefore requires immediate surgical intervention. Following symptoms indicate towards more serious situation requiring medical treatment :
- Baby is in obvious pain
- Baby starts vomiting suddenly
- The bulge is swollen and pains in touch or is discolored.
Diagnosis of Umbilical Hernia
Physical examination is often performed by the doctor to determine whether the infant or adult has an umbilical hernia or not. In the physical examination, the doctor observes the hernia by pushing it back in the abdominal cavity to check if it is reducible or if it is trapped in its place (incarcerated). An incarcerated hernia can cause serious complications as this trapped part can be derived from a blood supply which may result in permanent tissue damage.
Other than the physical examination, X-ray or ultrasonography of the abdominal area may also help in determining the complications. Blood tests may also help to confirm whether it is associated with any kind of infection or ischemia.
Complications of Umbilical Hernia
Complications are usually not seen in children. But some complications can be seen in the incarcerated type of umbilical hernia. This is because intestines here cannot be pushed back and thus this leads to loss of blood supply to them which causes pain or ischemia of the tissue. Abdominal hernias involving strangulated intestine requires immediate surgery as an intervention. Symptoms of strangulated umbilical hernia are :
- Fever
- Constipation
- Nausea with vomiting
- Severe abdominal pain
- Bulging of a lump in the abdomen
Treatment of Umbilical Hernia
In children, the umbilical hernia often heals on their own, but in adults, surgery is performed to avoid any kind of complication. Surgery is not performed until the hernia :
- Turns painful
- Is larger than one-half inch of diameter
- Does not shrink within a year
- It does not heal itself until the child turns 4 years old.
- Becomes trapped or blocks the intestine
Surgery for Umbilical Hernia
The umbilical hernia repair is a surgery performed to fix the umbilical hernia. It can be performed in two ways :
- Open hernia repair
- Laparoscopic hernia repair
Open Hernia Repair
It is a conventional surgery in which the surgeon makes an incision around the belly button to access the hernia over the bulge site.
Laparoscopic Hernia Repair
It is a less invasive procedure. Small incisions are made by the surgeon over the bulge site of the hernia. Then a long, thin tube along with a lighted camera is inserted in the incision. This instrument is known as the Laparoscope, which allows the surgeon to see the abdominal cavity on the video screen.
The main aim in both of the surgeries is to place the bulging intestine back into its place through the hole and then close the incision. Sometimes, synthetic mesh is being inserted in the abdomen to strengthen the weakened area.
Conclusion
The majority of children will recover from the umbilical hernia on their own by age of 3 or 4. But if it persists for more than this or causes pain or discomfort, it is better to consult a pediatrician. The hernia repair surgery is a simple procedure and is very common. After surgery, it is recommended not to indulge one in any heavy physical activity for at least three weeks.